Address: Unit 608, No.6 Hongmian Dao, Futian Free Trade Zone, Shenzhen, China
Tel: +86(755)33223973
Fax: +86(755)33223977
Email: info@discturnkey.com
WhatsApp: +86-132-6677-1113
What is Reverse Logistics (RL)?
Many organizations and individuals have tried to define Reverse Logistics. We refer to the term "reverse logistics" as all activity associated with a product/service after the point of sale, the ultimate goal to optimize or make more efficient aftermarket activity, thus saving money and environmental resources.
The chart below shows how Reverse Logistics comes into play in the Supply Chain.
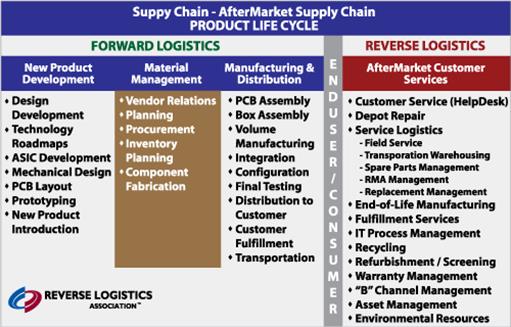
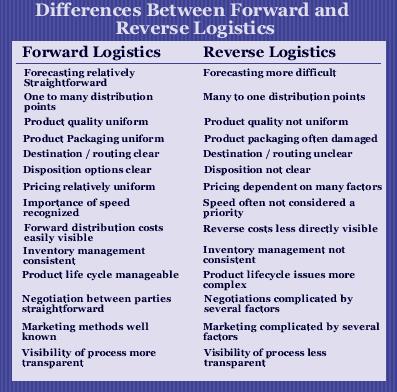
Other terms synonymous to Reverse Logistics (RL) are Aftermarket Logistics, Retrogistics, or Aftermarket Supply Chain. The reverse supply chain is also a term used in the industry. RL is not to be confused with forward logistics or getting the product to market commonly known as the forward supply chain. Types of activity common with reverse logistics includes: logistics, warehousing, repair, refurbishment, recycling, e-waste, after market call center support, reverse fulfillment, field service and many others.
Aftermarket Supply Chain
The aftermarket supply chain refers to an activity or period in time in the product life cycle after the product leaves the shelf, reaches the consumer and then is delivered for reuse in one form or another to the end consumer. This is synonymous with Reverse Logistics.
"In other words, anytime money is taken from a company's Warranty Reserve or Service Logistics budget, that is a Reverse Logistics operation"
- Gailen Vick, President of Reverse Logistics Association (RLA)